| On this page |
In order to use Houdini Engine, a Houdini Engine session needs to be created. Creating the session will load the necessary Houdini libraries and plug-ins, and setup Houdini Engine according to various preferences, and environment variables.
Socket ¶
Socket session was added when thin client was introduced in Houdini Engine. In short, thin client allows the main Houdini Engine processing to happen in a separate process, outside of the Maya process. For socket sessions, TCP socket is used to communicate between the Maya process and the Houdini Engine process.
In order to use socket sessions, the Houdini Engine server must be manually started with a known port on a known machine. Then, the host and port information is entered into the plug-in.
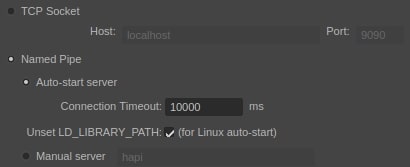
Named Pipe ¶
Named pipe session was added when thin client was introduced in Houdini Engine. In short, thin client allows the main Houdini Engine processing to happen in a separate process, outside of the Maya process. For named pipe sessions, named pipe is used to communicate between the Maya process and the Houdini Engine process. This is the recommended method when using thin client in the same local machine.
The named pipe session supports auto-starting the Houdini Engine server. When the plug-in initializes, the Houdini Engine server will be automatically started, and a named pipe is automatically chosen. In some cases on Linux, we have found that there can be library conflicts if the LD_LIBRARY_PATH has been set, resulting in HARS failing to start. There is now a preference to unset LD_LIBRARY_PATH before starting the server (and restoring the value afterwards, of course). The preference is on by default, but if you need to pass LD_LIBRARY_PATH to engine, you can turn this preference off. Likewise, we have also found that conflicts may arise when PYTHONPATH is set. If you enable Unset PYTHONPATH, the PYTHONPATH variable will be cleared before starting the Houdini Engine server, as well as when assets are viewed in Houdini via the “View Assets in Houdini” menu item. This preference is off by default for backwards compatibility, and is present for all operating systems. The timeout for connecting to HARS can also be set. This is useful if Houdini takes a long time to start.
The Houdini Engine server can also be manually started with a known named pipe. Then, the named pipe information is entered into the plug-in.
Within Maya Process ¶
The Within Maya Process session type is no longer supported in Maya as of Houdini 17.0
Before thin client was added to Houdini Engine, creating a Houdini Engine session within the Maya process was how Houdini Engine was initialized. All the Houdini libraries and necessary files were loaded directly within Maya’s process. This required the libraries of Houdini, its plug-ins, and their library dependencies to be compatible with the libraries of Maya and its plug-ins. Otherwise, there could be dynamic library conflicts, library symbol conflicts, and crashes. Since the introduction of Houdini Engine, we have encountered additional issues and conflicts, and we are no longer able to support this session type.
If your session type optionVar is set to Within Process, Named Pipe with auto-start will be used instead. On some Linux systems, there may be problems with auto-start, in which case you will need to manually start HARS in order to connect to it.
OptionVars ¶
If loading the houdini plugin is not possible with the default settings due to library conflicts, the optionVars controlling the session type can be set manually before loading the plugin.
For a socket session, with the default port and host:
optionVar -iv "houdiniEngineSessionType" 1; optionVar -iv "houdiniEngineThriftPort" 9090; optionVar -sv "houdiniEngineThriftServer" "localhost";
For a named pipe session with autostart:
optionVar -iv "houdiniEngineSessionType" 2; optionVar -sv "houdiniEngineThriftPipe" "hapi"; optionVar -iv "houdiniEngineSessionPipeCustom" 0; optionVar -iv "houdiniEngineTimeout" 10000;
Server ¶
In order to use a socket session on the client side, you need to start the server executable HARS, included in Houdini installation. HARS is a console application with simple command-line arguments:
$ HARS -h
Allowed options:
-h [ --help ] Produce this help message
-s [ --socket-port ] arg The server port, if using a TCP socket session
-n [ --named-pipe ] arg The name of the pipe, if using a named pipe session
-a [ --auto-close ] Close the server automatically when all client
connections are closed
-r [ --ready-handle ] arg Event to signal when the server is ready to serve
(for automated server startup)HARS links directly to libHAPI and to core Houdini libraries and their dependencies. Since Thrift IPC is cross-platform, the server process (HARS) may be run on different platforms. The HARS server may also be used for a named pipe session when autostart is not specified. The port or pipe should match the one specified in the Houdini Engine preferences. Please see the Session section in the Houdini Engine Documentation for more details.
Note
The HARS server currently only supports a single client connection. If a client is connected to the server and another client tries to connect, then the second client will block until the first connection is closed.
Cleaning Up the Session ¶
If the server was set to autostart, unloading the plugin will terminate the server, and the houdini engine license will be released. The server will be restarted when the plugin is reloaded, and the server will acquire a license when the first asset is loaded.
If the HARS server is started manually, it will not be automatically killed unless the auto-close option was set (and assuming that no other client was connected to the server).
If the HARS server has been running for a while, it may get cluttered up with input and merge nodes belonging to deleted maya nodes still on the undo queue. Flushing the undo queue from time to time will ensure that those nodes are deleted.