| On this page | |
| Since | 17.0 |
Overview ¶
USD supports two types of instancing: instanceable primitives (where multiple copies of the same branch are aliases to shared storage) and point instancing (where USD stores points and prototypes to copy onto the points, but only draws the copies at render time). See USD instancing for more information.
This node can do both types of instancing: it can create a point instancer, or it can place instanceable prims based on the locations of points. (It can also reference in real separate copies instead of instanceable prims.)
The thing or things you want to create multiples of are called the prototypes. This node assumes the prototypes already exist, connected to the first or second input.
The points you want to instance/copy onto are called the targets. The targets can be points or prim positions in the input scene graph tree, or you can generate them in the SOP subnet inside this node, or in a SOP node elsewhere in the node hierarchy.
Example ¶
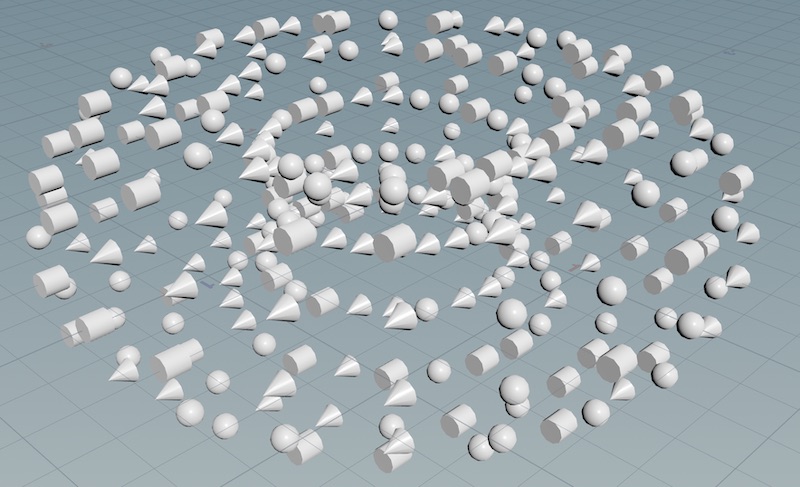
-
In the network editor, use the ⇥ Tab menu to create a Torus.
The “Torus” tool actually creates a SOP Create node that imports the result of a
Torus SOP into USD.
On the SOP Create node, set the Import path prefix to
/Geometry/torus. -
Add a
Sphere LOP. Set the Primitive path to
/Geometry/balland the Uniform scale to0.05. -
Add a
Cone LOP. Set the Primitive path to
/Geometry/coneand the Uniform scale to0.05. -
Add a
Cylinder LOP. Set the Primitive path to
/Geometry/tubeand the Uniform scale to0.05. -
Add an Instancer LOP.
-
Set the Primitive path to
/Geometry/shapes. -
Set the Method to “Point instancer”.
-
Set the Location source to “First input’s points”.
-
Set the Location primitives to
/Geometry/torus/mesh_0. -
Set the Prototype source to “First input”.
-
Set the Prototype primitives to
/Geometry/ball /Geometry/cone /Geometry/tube. -
Set the Prototype index to “Random”
The node randomly instances a ball, cone, or tube at each point of the torus.
-
Special SOP attributes ¶
-
You can create a
usdvisibilitypoint string SOP attribute to control the visibility metadata of the corresponding USD prim or point instance. The value should be eitherinvisibleorinherit.If you create point instances, this visibility information is converted to an
invisibleIdsUSD attribute.
How to ¶
| To... | Do this |
|---|---|
|
Scatter each prototype’s variant |
|
Parameters ¶
Primitive Path
The scene graph path at which to create the point instancer prim (when Method is “Point instancer”), or the parent of all created prims (when Method is anything other than “Point Instancer”).
Primitive Kind
If the prim at Primitive path doesn’t exist, this node creates it. If it creates the prim, it sets this as the prim’s kind.
Method
See Instancing in USD for more information.
Point Instancer
Create a point instancer. This is a single prim (with the prototypes as children) that draws the instanced geometry on-demand in the viewer or renderer.
Instanceable Reference
Creates an instanceable prim at each point. These are separate prims in the scene graph tree, and can individual overrides on each top-level prim, but they share a “shadow” copy of their descendant prims, so their descendants are not editable or individually override-able.
Reference
Creates a separate prim at each point that references in the “prototype” prim(s). These references take up more storage space than instanceable prims, but you can edit/override the descendant prims.
Instanceable Inherit
Just like “Instanceable Reference” except the instance primitives inherit from the source primitive rather than reference it.
Inherit
Just like “Reference” except the instance primitives inherit from the source primitive rather than reference it.
Instanceable Specialize
Just like “Instanceable Reference” except the instance primitives specialize from the source primitive rather than reference it.
Specialize
Just like “Reference” except the instance primitives specialize from the source primitive rather than reference it.
Set Extents
Compute the extents (bounding box) of the instanced geometry and store this on the instancer prim.
Location Source
Where to get the points to copy onto.
Internal SOP
Build a SOP network in the subnet inside this node to generate the points.
External SOP
Get the points from the output of a SOP elsewhere in the Houdini node hierarchy.
First input’s primitives
Use the positions of primitives in the first input as the target points.
First input’s points
Get the points from a geometry prim, or the positions from another point instancer in the first input.
SOP Path
When Location source is “External SOP”, the node path of the SOP node that generates the target points.
Point Group
When Location source is “Internal SOP” or “External SOP”, get the points from this named group in the SOP geometry.
Location Primitives
When Location source is “First input’s primitives”, this is the scene graph paths of the primitives whose positions you want to use as target points. When Location source is “First input’s points”, this is a the scene graph path(s) of one or more geometry prims containing target points (such as a polygonal mesh). In either case you can use pattern syntax to select multiple primitives.
Prune Mode
You can delete or hide a certain percentage of the target points. This may be useful if the target points come from an overly dense point cloud, or to speed up display when you're first setting up the instancer. The default is “None” to not delete or hide any points.
Prune Amount
When Prune mode is “Delete” or “Set visibility”, the percentage of points to delete or hide. This can be used to improve performance while setting up the operator.
Set Orientation
Rotate the instanced primitives based on standard instancing SOP attributes on the points. These SOP attributes include N, up , and orient.
Set Scale
Scale the instanced primitives based on standard instancing SOP attributes on the points. These SOP attributes include scale and pscale.
Make Transform Source Primitives Invisible
Set the visibility of the Location primitives to “hidden” in the output. The default is on.
Point Attributes to Copy
A list of attributes on the template points to copy to instances. When creating a Point Instancer, an array primvar will be created for each listed attribute, with an entry for each point’s value. When creating reference primitives, an attribute of the same name and type will be created on each primitive.
These parameters are visible when Method is “References” or “Instanceable references”.
Instance Base Name
A prefix string for the names of prims created by this node. The node appends the point index to this string to create each name. This name is then appended to the Primitive path value to create the reference prim path. This is ignored if Use path attribute is on (below) and the path attribute exists.
Use Path Attribute
Use a string attribute on the target points to create the reference prim path.
Make Primitive Paths Unique
When Use path attribute is on, if a path attribute is not unique append an identifier to ensure uniqueness.
Path Attribute
When Use path attribute is on, the name of a string attribute on each point containing the path to use for the prim created at that point. The path in this attribute is appended to the Primitive path value. If this attribute doesn’t exist, the node falls back to using Instance base name.
If the paths in the attribute aren’t unique, and Make primitive paths unique is off, the node will only create one reference per path. In this case the node will show a warning.
Prototype Source
Whether the prim(s) you want to reference/instance onto the points is/are in the first input or the second input.
Create Prototypes Area
If Prototype Source is First Input, this toggle controls whether to create a “Prototypes” scope under the specified Primitive Path or not.
If enabled, the primitive will be populated with references (see Prototype Reference Type below) to the original source primitives, and these references will be used for the instances. If disabled, the instances will be directly connected to the original source primitives. It is standard practice, but not required, to have this enabled when the Method is set to Point Instancer.
Prototype Reference Type
If Prototype source is “First input” and Create Prototypes Area is enabled, this parameter controls the composition type to use when creating references to the source primitives from within the “Prototypes” folder in the scene graph. This parameter can be “Reference”, “Inherit”, or “Specialize”. See inherits and specializes for more information about how these choices differ from a simple reference.
Make Prototype Source Primitives Invisible
If Prototype source is “First input” and Create Prototypes Area is enabled and this is on, the node sets the visibility of the prims used as primitives to “hidden” in the output. The default is on.
Use Entire Stage as Prototype
If Prototype source is “Second input” and this is on, the node copies everything from the second input’s scene graph tree under a new prim and uses that as the prototype. This lets you build a node chain that builds the prototype and connect it to the second input, and not have to specify which prim in the second input to use.
Only Copy Specified Prototype Prims
If Prototype source is “Second input” and Use Entire Stage as Prototype is off, this controls whether to only copy the prototype primitives specified by Prototype Primitives, or the entire stage. The default is on.
Using this option can result in a smaller stage, but requires that the prototype sources are fully self-contained (for example they cannot refer to materials that sit elsewhere in the prim hierarchy).
Allow Prototype Primitives That Don’t Exist
This option allows the Prototype Primitives pattern to consist of a hard coded list of paths, where prims may not exist at all of the specified source locations. This works with prototype primitives coming from either the first or second input. Rather than generate an error or warning about missing prototype primitives, the node will do one of two things. If the destination prototype primitive already exists in the scene graph, this node does nothing to this existing primitive. The existing primitive at the prototype location is used as one of the instancer prototypes. If there is no primitive at the destination prototype location, then this node will create an empty typeless primitive at the required destination prototype location.
This mode is useful when adding prototypes to an existing point instancer.
Prototype Parent Kind
When Use entire stage is on, this sets the kind of the prim the node creates as a parent for root prims from the second input. The default is None.
Prototype Primitives
The scene graph path(s) of the primitive(s) you want to use as prototype(s). You can use pattern syntax to select multiple primitives.
Prototype Index
Random
Choose the prototype at each point randomly.
Index
Specify a single prototype to use at each point in a parameter. This lets you drive the parameter using an expression (for example, based on a context option).
Index Attribute
Use the value of an integer attribute on the target point as an index into the list of prototypes.
Name Attribute
Use the value of a string attribute to select the prototype by name. (The name of each prototype is copied from the original prim used to create the prototype. The node may add numbers to the prototype names to make them unique.)
Path Attribute
Use the value of a string attribute to select the prototype by path.
Seed
When Prototype index is “Random”, the seed for the random number generator.
Index
When Prototype index is “Index”, the index of the prototype to use, from the list of primitives in Prototype primitives. You can use an expression to choose the index based on some other factor.
Index Attribute
An integer attribute on the target points that specifies the prototype to use.
Note
When Location source is “First Input’s Points”, the USD Prim(s) will be checked first for a matching attribute and, failing that, a matching primvar.
Name Attribute
A string attribute on the target points that specifies the name of the prototype to use.
Note
When Location source is “First Input’s Points”, the USD Prim(s) will be checked first for a matching attribute and, failing that, a matching primvar.
Note
USD Point Instancer primitives don’t inherently have the ability to address prototypes by name. This node finds the prototype by name, then sets the corresponding index in the protoIndices array attribute on the point instancer prim.
Path Attribute
A string attribute on the target points that specifies the path of the prototype to use.
Note
When Location source is “First Input’s Points”, the USD Prim(s) will be checked first for a matching attribute and, failing that, a matching primvar.
Warn on Skipped Instances
When Prototype Index is “Index Attribute”, “Name Attribute” or “Path Attribute”, this toggle controls whether or not to emit a warning when an instance is skipped due to there being no match between the attribute data and the prototype list.