Parameters ¶
Transform ¶
Transform Order
The left menu chooses the order in which transforms are applied (for example, scale, then rotate, then translate). This can change the position and orientation of the object, in the same way that going a block and turning east takes you to a different place than turning east and then going a block.
The right menu chooses the order in which to rotate around the X, Y, and Z axes. Certain orders can make character joint transforms easier to use, depending on the character.
Translate
Translation along XYZ axes.
Rotate
Degrees rotation about XYZ axes.
Pivot
Local origin of the object. See also setting the pivot point .
Modify Pre-Transform
This menu contains options for manipulating the pre-transform values. The pre-transform is an internal transform that is applied prior to the regular transform parameters. This allows you to change the frame of reference for the translate, rotate, scale parameter values below without changing the overall transform.
Clean Transform
This reverts the translate, rotate, scale parameters to their default values while maintaining the same overall transform.
Clean Translates
This sets the translate parameter to (0, 0, 0) while maintaining the same overall transform.
Clean Rotates
This sets the rotate parameter to (0, 0, 0) while maintaining the same overall transform.
Clean Scales
This sets the scale parameter to (1, 1, 1) while maintaining the same overall transform.
Extract Pre-transform
This removes the pre-transform by setting the translate, rotate, and scale parameters in order to maintain the same overall transform. Note that if there were shears in the pre-transform, it can not be completely removed.
Reset Pre-transform
This completely removes the pre-transform without changing any parameters. This will change the overall transform of the object if there are any non-default values in the translate, rotate, and scale parameters.
Keep Position When Parenting
When the object is re-parented, maintain its current world position by changing the object’s transform parameters.
Child Compensation
When the object is being transformed, maintain the current world transforms of its children by changing their transform parameters.
Enable Constraints
Enable Constraints Network on the object.
Constraints
Path to a CHOP Constraints Network.
Tip
You can you use the Constraints drop down button to activate one of the Constraints Shelf Tool. If you do so, the first pick session is filled automatically by nodes selected in the parameter panel.
Note
Lookat and Follow Path parameters on object nodes are deprecated in favor of Look At and
Follow Path constraints.
The parameters are only hidden for now and you can set their visibility if you do edit the node’s parameter interface.
Render ¶
Display
Whether or not this object is displayed in the viewport and rendered. Turn on the checkbox to have Houdini use this parameter, then set the value to 0 to hide the object in the viewport and not render it, or 1 to show and render the object. If the checkbox is off, Houdini ignores the value.
Set Wireframe Color
Use the specified wireframe color
Wireframe Color
The display color of the object
Viewport Selecting Enabled
Object is capable of being picked in the viewport.
Select Script
Script to run when the object is picked in the viewport. See select scripts .
Cache Object Transform
Caches object transforms once Houdini calculates them. This is
especially useful for objects whose world space position is
expensive to calculate (such as Sticky objects),
and objects at the end of long parenting chains (such as
Bones). This option is turned on by default for Sticky and
Bone objects.
See the OBJ Caching section of the Houdini Preferences window for how to control the size of the object transform cache.
View ¶
Icon scale
Scales the viewport geometry. This parameter is only for display purposes.
Resolution
The output resolution in pixels. Standard presets are available via the pull down menu to the right of the parameter.
Pixel aspect ratio
The pixel aspect ratio of the output image.
Projection
Type of camera projection used for rendering (for example, perspective or orthographic).
Perspective
This simulates the classic pinhole camera where camera rays emanate from a common camera origin through a flat camera plane.
Orthographic
This uses parallel camera rays that are orthogonal to the (flat) camera plane. The width of the view volume is determined by the Ortho Width parameter below.
Polar (panoramic)
This projection uses a spherical camera plane for rendering.
Cylindrical (panoramic)
This projection uses a cylindrical camera plane for rendering.
Lens Shader: Use a lens shader to initialize rays for ray tracing.
Selecting Polar, Cylindrical or Lens Shader will automatically switch the Rendering Engine (on the output driver) to Ray Tracing, as it is impossible to render these projections with micropolygon rendering.
Lens Shader
Specifies the CVEX lens shader to use for the Lens Shader projection
type. A lens shader is responsible for computing primary rays from
screen coordinates, and is a flexible way to define new kinds of camera
projections that can’t be modeled as perspective or orthographic
projections. Lens shaders can have the following parameters and
exports:
float x
X screen coordinate in the range -1 to 1.
float y
Y screen coordinate in the range -1 to 1.
float Time
Sample time.
float dofx
X depth of field sample value.
float dofy
Y depth of field sample value.
float aspect
Image aspect ratio (x/y).
int xres
Image horizontal resolution.
int yres
Image vertical resolution.
export vector P
Ray origin in camera space.
export vector I
Ray direction in camera space.
export int valid
Whether the sample is valid for measuring.
The lens shader should be able to handle x and y values outside the -1 to 1 range, in case samples outside the image need to be generated. The P and I exports should be created in camera space, ignoring the camera transform.
Before rendering begins, mantra measures the lens shader before
rendering. During the measuring process, the valid variable can be used
to flag invalid rays. In the future, the valid flag may be used during
rendering.
Mantra’s camera space is defined with positive z-values in front of the camera, so for a default camera the z-axis is flipped relative to Houdini’s world space.
An example lens shader is the Ray Lens shader.
Focal length
Camera focal length (zoom).
Focal units
The units used for the focal length.
Aperture
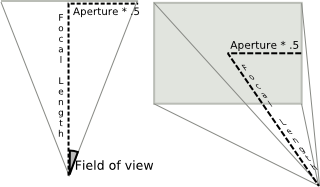
Width of the visible field.
You can obtain a good fit between the Houdini camera and a real world camera by matching a measured lens’s horizontal angle of view, and deriving a Houdini focal length value that reproduces it with the default aperture 41.4214.
Note
The default aperture combined with the default focal length of 50mm produces a 45 degree field of view.
Otho width
Width of orthographic view volume when using Projection is set to Orthographic.
Near clipping
Position of near clipping plane.
Far clipping
Position of far clipping plane.
Screen window X/Y
Define the center of the window during the rendering process.
Screen window size
Scale for expanding the cropped area specified by the Crop parameters.
Screen window mask
Sets the screen window mask to cover the bounding box of the selected object(s).
Left crop
Left cropping margin for camera’s view area.
Right crop
Right cropping margin for camera’s view area.
Bottom crop
Bottom cropping margin for camera’s view area.
Top crop
Top cropping margin for camera’s view area.
Crop Mask
Sets the pixel crop region to cover the bounding box of the selected object(s).
Note
You can optionally add the spare parameter Visible Objects (vobject) from the Parameter Interface. This allows you to control which objects are displayed in the viewport when looking through the camera.
Sampling ¶
Shutter time
The shutter time refers to the portion of a frame the shutter is actually open. On a physical camera, this if often referred to as Shutter Speed. The renderer uses this determine motion blur. The value should be in the range [0,1].
A value of 0 for the shutter time would mean that there is no motion blur at all, as the shutter is only “Open” for an instant. A value of 1 on the other hand would mean that the shutter is open for the entire length of the frame.

In the above example the sphere is rotating a full 360 degrees over the course of a single frame. You can see how the length of the “motion trail” or “blur” changes based on the shutter time. In most cases, the default value of .5 is appropriate for animated sequences and a good match for real world settings.
Keep in mind that this parameter controls the amount of time within a single frame, that the shutter is open. It does not refer to how long an individual frame is. To adjust the frame rate, change the Frames per Second parameter in the Global Animation Options.
Focus distance
The lens focal distance and distance from the camera at which objects will be in focus. This is only used when rendering using depth of field. Objects outside this distance will be blurred.
F-stop
Lens fstop. This is only used when rendering using depth of field. Determines blurriness of depth of field effects.
Bokeh
Filter kernel used in depth of field rendering. Use the pop-up menu to the right of the text box to choose from the available options.
Radial bokeh (radial)
Use a gaussian filter kernel (highest quality).
Image file bokeh (file)
Use an image file
Box filter bokeh (box)
Use a box filter kernal.
Disable bokeh (null)
Do not filter.
Bokeh image file
The file to use for “file” shaped bokeh. White/black cutout images that delineate the shape of the lens are good candidates, where white regions represent the areas that light passes through.
Bokeh rotation
The rotation for “file” shaped bokeh.
For information on transforming sub-cameras, see the Stereo Camera Rig help.