| On this page |
Input ¶
You can import instancers to Houdini when you select the Actor with the Instanced Static Mesh ComponentThe instanced mesh is imported as a packed primitive, copied on each of the instanced points.
Each material used for the instances will have a corresponding attribute named unreal_materialINDEX where INDEX is the index of the corresponding material’s slot. The value will be the Unreal path to that material.
Foliage instances can be imported in a similar way, and will have the unreal_foliage attribute set.
Alternatively, you can import a Static Mesh as a single attribute instance when checking the Import as reference checkbox.
Output ¶
The plug-in supports outputting instances from an asset using packed primitives, object instancers, or attribute instancers.
Instanced geometries in Unreal are InstancedStaticMeshComponents by default or HierarchicalInstancedStaticMeshComponents if the geometry instanced has multiple LODs. If you want to force the creation of HierarchicalInstancedStaticMeshComponents, even without LODs, you can add the unreal_hierarchical_instancer attribute and set its value to 1.
Instanced geometry or uassets appear as instancers in the Houdini Outputs section of the Detail Panel, as shown below:
Point attributes can be added to specify material overrides for the instanced meshes. Create an attribute named unreal_materialINDEX where INDEX represents the material slot index to override. The value should be the Unreal path to the material to be used.
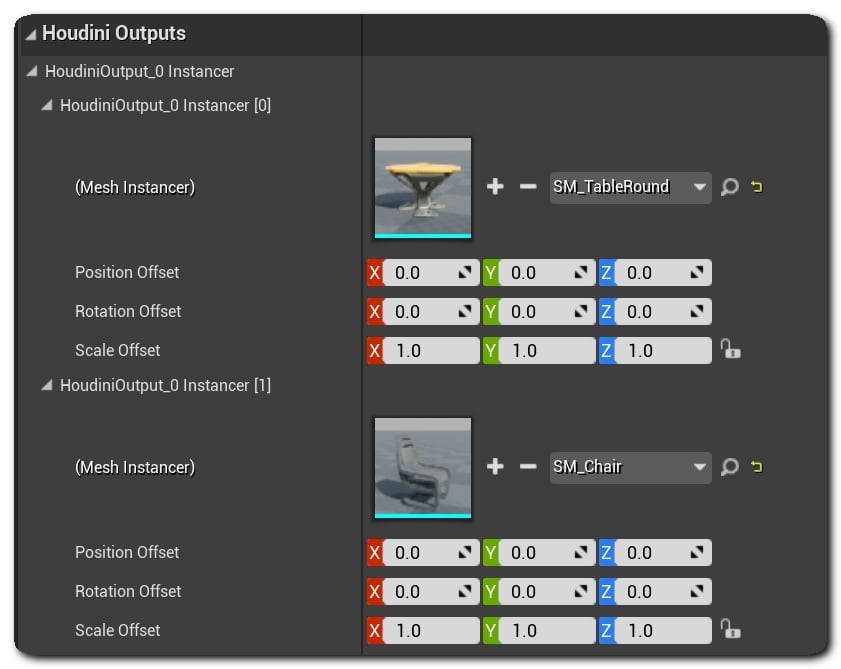
The geometry on each instanced output can be replaced in Unreal. It can have a position, rotation, and scale offset applied to it using the corresponding controls in the detail panel.
Packed Primitives ¶
The recommended way to create instances is using Packed primitives. The packed geometry is used as the instanced geometry and any copy of this packed primitive is converted to instances in Unreal.
Note
An instancer is created for packed primitives only if that packed primitive is copied more than once. Single instance instancers only create regular Static Mesh Components.
A simple way is to use a Copy To Points SOP and turn on the Pack and Instance option. You can also use Pack Geometry Before Merging or Inputs.
It’s important to look at the location of the attributes when you control properties of either the instancer of the instanced mesh in packed primitives. If you apply an attribute before packing it’s applied to the generated mesh. For example, you apply attributes before using the PACK SOP. If you apply attributes after packing, it’s only applied to the instancer.
Object Instancers ¶
You can also create Instancers using the instance Object node.
Note
It’s recommended to use packed primitives or atrributes instancers instead of Object Instancers.
Attribute Instancers ¶
Besides instancing geometry generated by the HDA, instances can also be created from pre-existing Unreal assets.
This can be done using the unreal_instance attribute and setting the attribute value to the asset’s reference.
You aren’t limited to static meshes, but the instanced asset must be convertible to a native Actor type. In that case, multiple instances of that Actor type is created and the generated instancer component will be a HoudiniInstancedActorComponent. This can be used to spawn pre-existing assets in the level using the generated instancer’s point cloud.
You can also instantiate classes directly by using attribute instancers. This is useful to create instances of a class which you can’t save as a Uasset in the Content Browser, but can be instaniated as an Actor(for example, Lights, Volumes etc.. ).
To do so, set the unreal_instance value to the clsas name you want to instantiate as Actor (unreal_instance = PointLight).
Note
To detect it properly, attribute instancers need to be in a separate part of the Geometry. Attribute instancer won’t be detected if the points that they are assigned to is part of the main geometry.
When an asset referenced by an attribute instancer could not be found, the plugin creates a default “asset not found” box mesh (hidden in-game by default) instead of ignoring the instancer. This can be enabled or disabled in the plugin settings in the Show default Mesh checkbox.
You can apply the Houdini rot/orient and scale attributes to specify the transform of the instance.
Splitting Instancers ¶
There are some cases where you may want to split instancer outputs to multiple components. This could be to assign different materials to each instancer or to get a finer grain control on the actors generated when baking.
This can be done using the unreal_split_attr string attribute. This attribute’s value should be set to the name of another attribute, whose values will be used to control the splitting.
(a separate instancer component will be created for each value of that attribute).
For example, you can use the unreal_material attribute as the unreal_split_attr attribute (unreal_split_attr = unreal_material) creates an instancer component for each material on the second attribute.
If three different materials are used, the instancer splits to three different instancer components.
In Houdini 20.5, using the unreal_split_instances attribute to create individual StaticMeshComponentshas been deprecated and will be removed in a future version.
It’s recommended to use the unreal_split_attr attribute instead.
The following code provides a behaviour similar to the unreal_split_instances attribute:
i@id = @ptnum; s@unreal_split_attr = "id";
Overriding - DEPRECATED ¶
The geometry that is instanced is shown in a thumbnail picker. You can override it by pressing the drop down asset chooser to pick an asset from the list, or by dragging and dropping an asset from the content browser over the thumbnail.
If the geometry used by an instancer output is overridden with something other than a static mesh or vise-versa, the corresponding component will be changed accordingly. For example, you can choose a ParticleSystem asset, which results in AEmitter objects spawned at instance points. Likewise choosing a Blueprint asset will spawn Actor instances of that Blueprint.
In Houdini 20.5 the UI for overriding instances is disabled by default, but can be re-enabled from Unreal plugin settings under “Enable Deprecated Instance Variations”.
Variations - DEPRECATED ¶
Controlling instance variations from Unreal has been deprecated in Houdini 20.5 and will be removed in a future version.
Projects that use this feature should migrate variation logic to Houdini before the next release, when the processing of HDA variations will be removed.
In Houdini 20.5 the UI for controlling instance variations is off by default. You can turn it on from Unreal plugin settings in Enable Deprecated Instance Variations.
Per Instance Custom Data ¶
Per instance Custom Data lets you add custom data to the instance buffer, that can then be read by the instancer’s material’s vertex shader.
In your HDA, you can specify per instance custom data on your instances, via attributes:
The number of custom floats per instance can be set via the unreal_num_custom_floats attribute.
The custom data itself can be set on the instances via unreal_per_instance_custom_dataX attributes, where X is the zero-based index of the custom float data.
An example is to specify custom RGB float values on instances.
You need to add:
i@unreal_num_custom_floats = 3; (to indicate that each instance will have 3 custom floats) f@unreal_per_instance_custom_data0 = XXX; (red value) f@unreal_per_instance_custom_data1 = YYY; (green value) f@unreal_per_instance_custom_data2 = ZZZ; (blue value)
Foliage Types ¶
To output foliage instances with an HDA, add the unreal_foliage attribute with its value set to 1 to the instances. UE5 requires a Foliage Type Asset stored in the Content folder to create foliage instances inside an Unreal level.
If the instance type in the HDA is set to reference an Unreal Static Mesh then the plugin will automatically create the needed Foliage Type assets when cooking and baking.
If the instance type is set to an existing Unreal Foliage Type, then foliage instances can be baked to that foliage type. During cooking, a temporary Foliage Type is created which is a copy of the user-defined Foliage Type specified in the HDA. This allows you to select existing or HDA generated foliage in the Foliage Editor after cooking. The instances are baked into the level using the target Foliage Type only during baking.
Note
If you modify the temporary Foliage Type, when you bake the HDA it creates a new Foliage Type. This prevents changes to the original Foliage Type.
The unreal_foliage_attachment_type attribute attaches foliage instances to other objects in the Unreal level. It can take the following values:
-
0 - The instance is not attached (default)
-
1 - The instance can be attached to any collision component.
-
2 - The instance can only be attached to landscape collision components.
The exact component to attach is determined by tracing a vertical ray up and down from above the instance’s position for a distance of unreal_foliage_attachment_distance.
Level Instancing ¶
Level Instancing is supported in Unreal 5.1 and later; set unreal_instance to reference the source level or packed level blueprint.
In Unreal, Level Instancing is at the Actor level, rather than the component level. Both cooking and baking generate Actors rather than Components.
Note
Unreal expects both the source and target levels to have certain settings such as Extenal Actors. It’s suggested to run a Map Check in Unreal when developing your HDA and instancing pipeline to make sure your data is compatible with the latest version of Unreal.
Attributes ¶
Houdini to Unreal ¶
This table lists special attributes to set in an HDA and the plugin recognizes when you translate the Houdini data to Unreal outputs. You can setup these attributes on your assets to control and override some properties and behaviours of the generated Unreal outputs. See Attributes and Groups for more information.
Instancers ¶
Attribute Name |
Owner |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
point, detail |
string |
Unreal path to an Asset that shall be instanced at the given transform. In version2, this attribute can also be a Class Name ( |
|
detail, prim, point |
int, float |
When used on instances (and set to 1), the plugin will add the instances to the current level’s foliage system instead of creating new actors/components |
|
point |
int |
Determines whether foliage should to attach to other objects in the level - 1 for yes, 0 for no, a value of 2 attaches to landscapes only. |
|
point |
float |
Distance to search vertically when using |
|
any |
string |
Indicates the name of another attribute to be used to split the instancers into multiple components depending on that second attributes values |
|
detail, prim |
any |
(deprecated) use unreal_split_attr instead - Indicates that the generated instances should be split into |
|
prim |
float(4) |
(deprecated) Used with unreal_split_instances to specify a per-instance color to override the generated StaticMeshComponents vertex colors |
|
any |
int |
When set to 1, forces the creation of HierarchicalInstancedStaticMeshComponent instead of |
|
any |
int |
When set to 1, forces the creation of an instancer component ( |
|
any |
int |
Indicates the number of custom floats to be used for an instancer’s Per Instance Custom Data |
|
any |
float |
Per-Instance Custom float data, where X is the zero-based index of the custom data |